Background of the Army
- 1959: Creation of the Cameroonian Army
- 1960-1962: Creation of the Military Sectors of the Centre, South and East (Yaoundé), Littoral (Douala), West (Dschang), North (Garoua) and West Cameroon (Buea);
- 1965: “Cameroonisation” of officials: appointment of a Cameroonian to the post of Commander of the Land forces;
- 1973: Creation of a command and administrative body called the Army and Combat Formations Command;
- 1976: Split of the Army Command into 06 distinct commands:
- Land forces Command
- Headquarters Command
- Schools and Training Centres Command
- Intervention Forces Command
- Military Engineering Command
- Signals and Cipher Command
- 1983: Creation of the Army Headquarters
- 2001: Reorganisation, professionalisation and rejuvenation of the Defence Forces in general and the Army in particular.
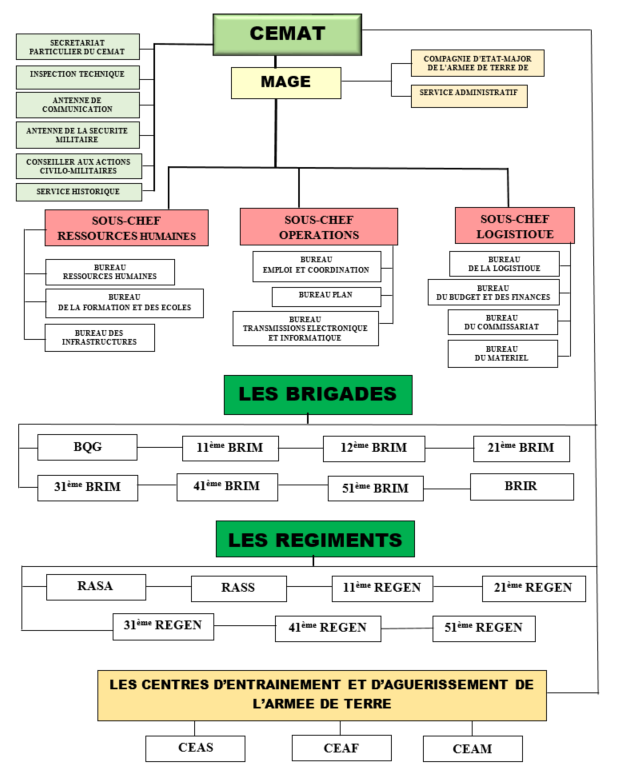
Organisation of the Army
The Army has two (02) main entities :
- An Army Staff :
The General Staff of the Army is placed under the authority of a Chief of Army Staff. He is assisted by a Major-General, who is responsible for coordination.
Army Forces
The Army Forces are professional units which participate with the other components of the Defence Forces in the defence of the vital interests of the Nation. They are made up of Combat, Intervention, Assistance and Support Formations and are divided into the following units:
They are made up of Combat, Intervention, Support and Assistance formations and are divided into the following units:
- The Headquarters Brigade (BQG);
- The Rapid Intervention Brigade (BRIR: BSA, BBR, BTAP);
- Motorised Infantry Brigades (BRIM);
- Rapid Intervention Battalions (BIR);
- Engineering Regiments (REGEN);
- Ground-to-Air Artillery Regiments (RASA);
- Ground-to-Ground Artillery Regiments (RASS);
- The Sahel Zone Training and Battle Inoculation Centre;
- The Forest Zone Training and Battle Inoculation Centre;
- The Mountainous Zone Training and Battle Inoculation Centre.
These Formations are located in five (05) Joint Military Regions (RMIA). Their command is dual. Organic command is exercised by the Chief of Army Staff, while operational command is exercised by the Commanders of the Joint Military Regions. These Joint Military Regions also exercise part of the organic command of these formations.
Organisational chart of the Army
Missions of the Army
- Contribute to the defence of territorial integrity;
- Participate in the general security of the national territory;
- Participate in preserving the continuity of government action and public services;
- Participate in law and enforcement operations under certain conditions;
- Participate in humanitarian or peacekeeping operations around the world.
Force deployment

Our weapons and services
Depending on their missions, modes of action and equipment, the personnel making up the Army’s formations belong to the following Arms and Services:
1°) Arms : infantry, armour and cavalry, artillery (ground-to-ground, ground-to-air), engineers, trains, signals;
2°) Services: police, justice, health, fuel, equipment, engineering.



